Photoinduced Geometrical Rearrangement of Lithium dDoped Argon Matrices
Abstract
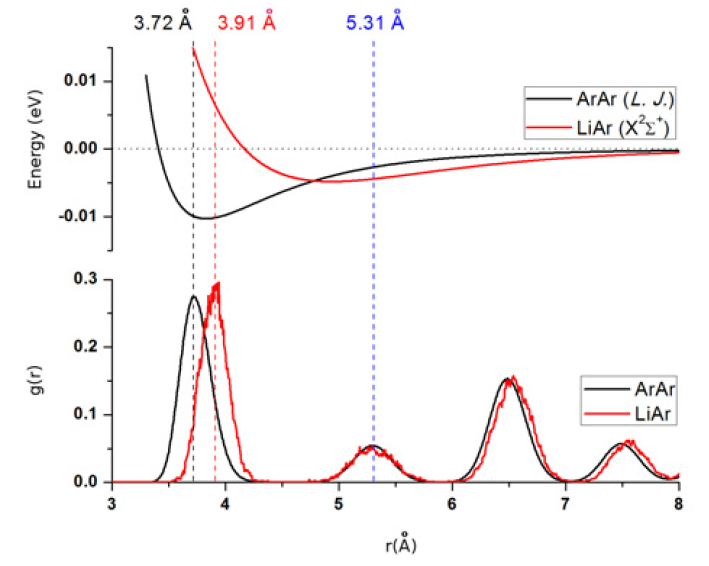
The energetics of Li(2p ← 2s) photoexcitation in low-temperature (T = 4 K) argon matrices is investigated via molecular dynamics simulations. Absorption and emission lineshapes are computed at the effective temperature of 31 K, which mimics zero-point energy effects on crystal site oscillations. Interaction forces are derived from an approximation to the energy of the electronic states of the doped solid, based on first order perturbation theory. The absorption band exhibit a three-fold structure, as a consequence of dynamic Jahn-Teller effect, the splitting being in close correspondence with available experimental results for this system. The relationship between transition energies and the photoinduced configurational rearrangement of the solid is also addressed. Lattice reorganization is found to be sensitive to the shallow long-range tail of the interatomic potentials, pointing to the feasibility to employ many-body response of doped matrices upon photoexcitation as a tool to study the topology of the excited electronic states of alkali-rare gas systems.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








