The Frederiks Transition in an Aqueous Clay Dispersion
Abstract
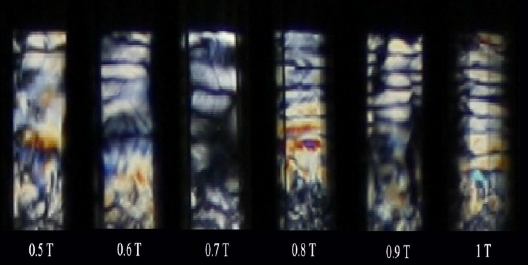
We show that under certain circumstances, aqueous dispersions of Na-fluorohectorite synthetic clay display transient spatially periodic structures when subjected to magnetic fields. These nematic structures result from the deformation of a uniform director pattern, a phenomenon which is known as the Frederiks transition. We study the samples between crossed polarizers, and present birefringence images of the particle reorganization as a function of time. Repeated measurements at different magnetic field strengths show that the threshold value for the inhomogeneous Frederiks transition with this setup is just below 0.5 T, and that the spatial wavelength of the structures decreases when the magnetic field is increased, as is expected.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








