Structural Studies of Mixed Nano-spheres and Polymers
Abstract
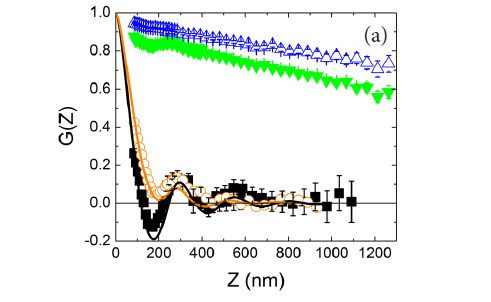
A newly developed neutron scattering technique known as Spin Echo Small Angle Neutron Scattering (SESANS) allows real-space density correlations to be probed in bulk samples over distances ranging from ~20 nm to up to several microns. We have applied this technique to study correlations between polymer-stabilized poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) spheres suspended in either dodecane or decalin. As expected, the data show that for colloid volume factions below about 40%, correlations between PMMA spheres are accurately described by the Percus-Yevick hard-sphere model. When a small amount of polymer is added to the colloidal suspension and when the carrier fluid is a good solvent for the polymer, short-range correlations between PMMA spheres are increased by the presence of the polymer depletant and are in reasonably agreement with calculations using an integral equation model. When higher concentrations of polymers are added, we find that long-range, power-law correlations develop between spheres, even though the sample flows freely. When the solvent is not a good solvent for the polymer depletant, correlations between PMMA spheres are unaffected by the addition of small quantities of polymer.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








