Weak Localization and Electron-electron Interaction in the Layered Compound CuFeTe2
Abstract
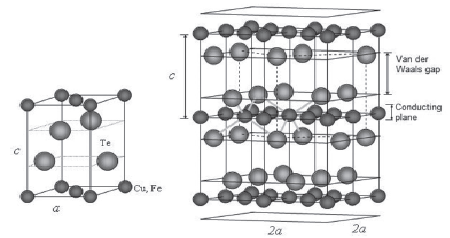
The study of the electrical properties of the layered compound CuFeTe2 shows that there are three well differentiated conduction regimes depending on the temperature. Below TSDW ~ 300 K the formation of a Spin Density Wave (SDW) state has been reported, in the frame of a metal to non metal transition. Below 100 K (~ TSDW/3) the behavior of the electrical resistance as a function of temperature and magnetic field is attributable to the still present not condensed electrons (quasi particles) in the SDW state. At low temperatures (1.8 - 20K), low current (< 1 mA) and magnetic eld (0<H <6 Tesla), the effects of weak localization and electronic interactions in two dimensions appear. At intermediate temperatures (20 < T < 100 K) a hopping conductivity behavior is observed.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








