Automated Detection of Thermoionic Currents in KCL: Sr2 + for Calibration of a Low Temperature Measuring Probe
Abstract
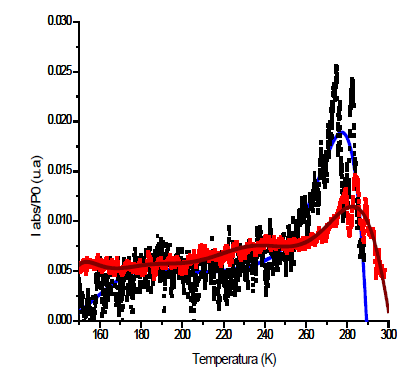
Induced Thermoionic Current (ITC) is a dielectric technique that has been successfully employed in the study of the defects responsible for the presence of different kinds of dipoles in diverse materials. Frequently these defects are associated with different properties as electrical, optical and others. In this work is shown the design and construction of automated homemade sonde for ITC measurements. The calibration of the measurement was carried out on KCl pellets (pure and doped with 0.053% mol of Sr2+) at low temperature over a “LabView-2009” platform. The influence and confirmation of the doping in the synthesized materials were evaluated by isothermal thermoluminescence (TL) at 513K. The TL measurement showed a substantial signal increment when the samples were doped. This doping generated an ITC Tm-signal at 247 K due to dipole reorientation of the IV (Sr2+-V’K) type. Furthermore, a peak associated to the interfacial polarization was detected. These defects appeared at a polarization voltage of 600 V and a heating rate of 17K/min.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








