Using the Rose Model in the Physical Analysis of Contrast Resolution for Two Computerized Tomography Technologies
Abstract
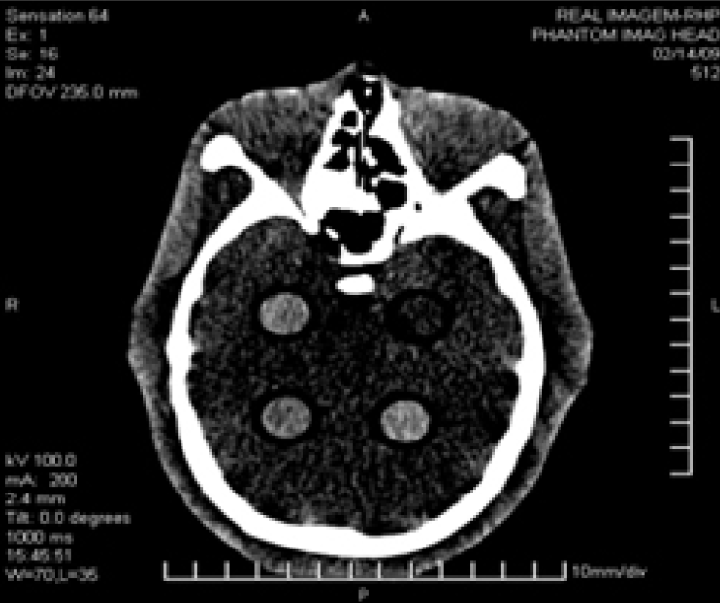
A study on image quality was developed using 28 tomographies collected to a head anthropomorphic phantom. The physical region of the phantom was used to analyze contrast resolution by their slices. The technologies used for tomographic acquisitions were a Philips Brilliance 6 and a Siemens Sensation 64. Tube current (mA), kVp, tomographic slice thickness and acquisition time per view were the scan variables changed among tomographies, looking for the best scan conditions which permit correct contrast resolution with the lowest dose for both technologies. Kerma-air in air was also measured and its index Ca,100 (mGy) was calculated as dose indicator. Contrast resolution and detection limits of both CT machines for brain studies were studied with the Rose Model application. Traditional objective image quality metrics as contrast to noise ratio (CNR) and global signal to noise ratio (SNR) were calculated over the tomographic images and also a visual expert analysis was done to compare both with model results. The study showed that is possible to reduce the dose, reducing mainly the mAs, without affecting contrast resolution in both technologies monitored. An optimized acquisition protocol is then proposed for each one.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








