Epicenter Diffusion: Dynamic Network Model
Abstract
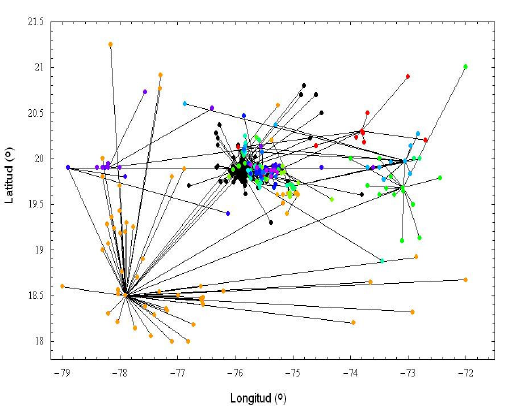
The diffusive behavior of replica secondary earthquakes taking place in Cuba from 1964 to 2000 was determined. Results show that takes place a process of epicenter centralization from the farther points towards the main earthquake impact point. The process is that of an anomalous diffusion in a sub-diffusive regime with exponential constant α = 0.24. It is shown a connection between the probability distribution for localizing the epicenters at a given distance of the main earthquake in the cell with the theoretical results of the Fokker-Planck (EFFP) fractionary equation solution.
Published
Dec 1, 2006
How to Cite
GÁMEZ, R. et al.
Epicenter Diffusion: Dynamic Network Model.
Revista Cubana de Física, [S.l.], v. 23, n. 2, p. 86-92, dec. 2006.
ISSN 2224-7939.
Available at: <https://revistacubanadefisica.org/index.php/rcf/article/view/RCF_23_2_86>. Date accessed: 03 july 2024.
Issue
Section
Original Articles
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








