Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Characterization of a Solid-State Electrode with Potential Application in Pb2+ Ions Detection
Abstract
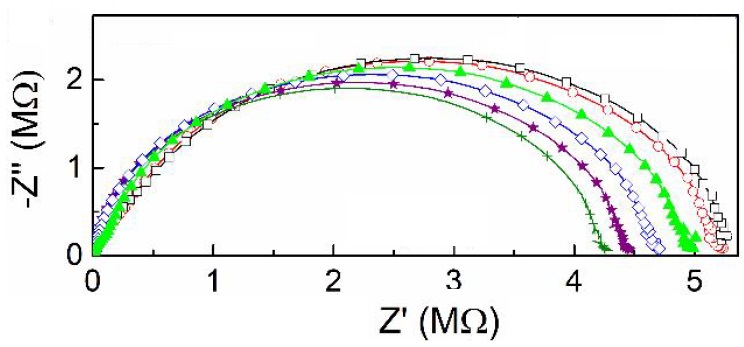
In this work, the characterization of a solid-state ion-selective electrode (SS-ISE) by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was performed for potential detection of Pb2+ ions. This electrode is based on a PVC-membrane with an aroylthiourea derivative as ionophore. The solid transducer was prepared using an epoxy-graphite-graphene composite. The impedance analysis (from 20 Hz-1 MHz) allows to describe the electrochemical response of the electrode in terms of the electrical processes in the membrane instead of the circuital elements related to the charge-transfer process at the transducer/membrane interface. The Pb2+ ions concentration was determined with this SS-ISE in aqueous solution by EIS using the electrical resistance of the membrane. The limit of detection reached by this approach was in the concentration range from 10-7-10-6 mol/L, one order of magnitude lower than the obtained by classical potentiometry. This analysis could be applied on the implementation of analytical determinations by EIS using SS-ISE.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0) license.








